How to choose optimal printer for colour labels?
Comparison of cost efficiency in choosing label print technology
Each of colour print technologies has its pros and cons. Production and delivery cost, quality, timing, label application area – all those factors need to be considered while choosing a certain method. Which one to choose, which will be best and will fit client’s expectations most? Etisoft, by investing and developing own technology makes it easier to maneuver within quality, delivery time and price of the label. At the same time it gives its partners wide help in choosing optimal printing method. It is worth remembering – low price does not always mean lower quality in this business. Not always, also, the bigger the volume, the lower price of the final product.
Etisoft has following print technologies in its portfolio:
- flexography
- HP Indigo (Digital toner inkjet)
- industrial inkjet
- desktop inkjet (Epson – Piezo technology, Kiaro – thermal print)
- thermo transfer (process tapes and spot ones)
- screen printing
- thermal inkjet print (HSA)
- offset (limited to printing instructions as booklets or sheets).
In this elaboration we compare most popular colour labels print technologies.
Flexographic print
It is a convex print with flexible print forms and liquid fast-drying paints technique which is universal enough to use it also on uneven surface. Despite many pros and using this technique as a standard one, this process is not the best of all. We obtain cost efficiency only with a high volume. It is therefore targeted to customers with high-volume delivery needs and strict quality requirements towards final product.
Advantages
- colour cohesion, vivid colours, high print quality and durability,
- the bigger label volume, the lower production cost,
- widest range of used materials.
Disadvantages
- relatively long realization time due to necessity to prepare and approve graphic design as well as order and make tools (polymer, punch),
- delivery time related to production capacity and machines availability,
- high storage cost,
- little flexibility in introducing fast changes into overprint area,
- no possibility to personalize each label.
Digital print (HP Indigo)
Digital print is meant when print content is delivered as computer data. This method is fast and comfortable, especially when we aim at low and medium volume. We can treat it both as a final method, and a “trial” print before high volume production.
Lead time for colour label is much shorter than in case of flexographic technology. Time saving is obtained by no need to prepare print forms (polymers and punches). On the other hand, production process needs to be consistent with the process of cutting labels form printed ribbon on laser or rotation machines. Hence, the process requires coordination between printing and cutting process on different printing machines.
Advantages
- short lead time (no need to irradiate polymer plates and prepare punch),
- print quality comparable to flexo labels,
- possibility to print little volume with little price,
- high print speed: up to 300 mm/s
- possibility to print on various surfaces
- print personalization (possibility to add serial numbering, variable data)
Disadvantages
- Lower print resistance to external factors than in case of flexo
- Technological limitations as for print material
- Lower range of available materials,
- Two-phase production cycle (printing machine and punching machine separately)
- Separate print process (roll-to-roll) and cutting labels in laser or rotation technique out of readymade, printed ribbon.
Inkjet print (industrial / desktop)
This is a kind of digital ink print using pigment inks or water-based inks. Dedicated materials are being used with mostly gloss paper. For those customers who require upgraded material durability or the overprint itself, dedicated synthetic materials (mainly polypropylene) is recommended. Every year we observe significant increase in multi-usage materials dedicated for this kind of print which indicates strong growth trend for inkjet technology. This market (including packages overprint) is expected to be growing by 15% annually within next few years. [1]
This technology for colour print is qualified for medium (industrial inkjet) and low labels volume (industrial inkjet and desktop). It is very flexible and efficient in terms of reaction to print (order date/production date/delivery date).
Advantages
- better management of print requirements: immediate readiness to print and possibility to act instantly,
- printing in full colour without dividing into stages for constant and variable data (numbering, barcode, etc.),
- printing exact number of labels needed by the customer (see table 1),
- printing speed: between 100 and 300 mm/s (printing speed depends on implied print quality and size of the label)
- attractive appearance of the label,
- optimization of warehouse management: limiting stock, scrap and production downtimes; no delays in deliveries,
- high quality of overprint – pigment inks are water and fading resistant, and so, they answer industrial clients’ needs,
- stable print cost,
- allows extensive patterns variability with the same label format,,
- time saving,
- for inkjet desktop: possibility to print manually from ERP system,
- possibility to set print up directly from device driver (no need to use dedicated software for label print).[2]
Disadvantages
- requires purchasing of the printer, necessity to prepare graphic design in proper resolution; labels print software, clean labels with proper base, systematic exchange of cartridges,
- responsibility for print is held by the customer,
- limited range of materials which coating is dedicated for inkjet adaptation (standard materials for flexography or thermo-transfer print are not suitable for inkjet),
- bigger volume does not contribute to the smaller price.
To sum up:
It must be underlined that in order to choose a proper technology for printing colour label, below factors must be taken into account:
- label purpose, i.e. its functionality, durability, internal or external application – quality requirements described in product specification by the customer,
- timeframe for implementation settled by the customer,
- labels volume (annually and per supply)
- target price (certain price cap of the label may limit economical reason for using certain technology),
- technological capacity of printing equipment,
- available range of materials within chosen printing technology,
- necessity to print variable data either eventually on a label, or its reprint by the customer.
Table 1. Comparison of colour print technologies efficiency
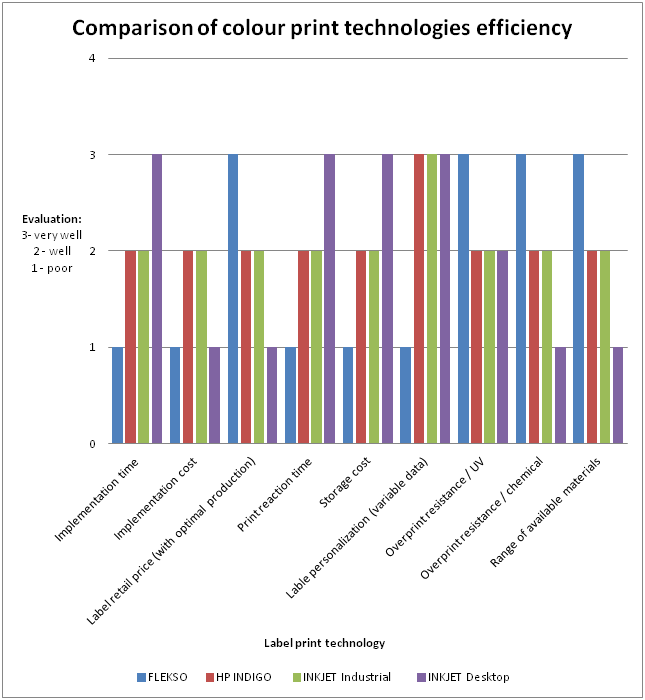
General efficiency comparison between technologies
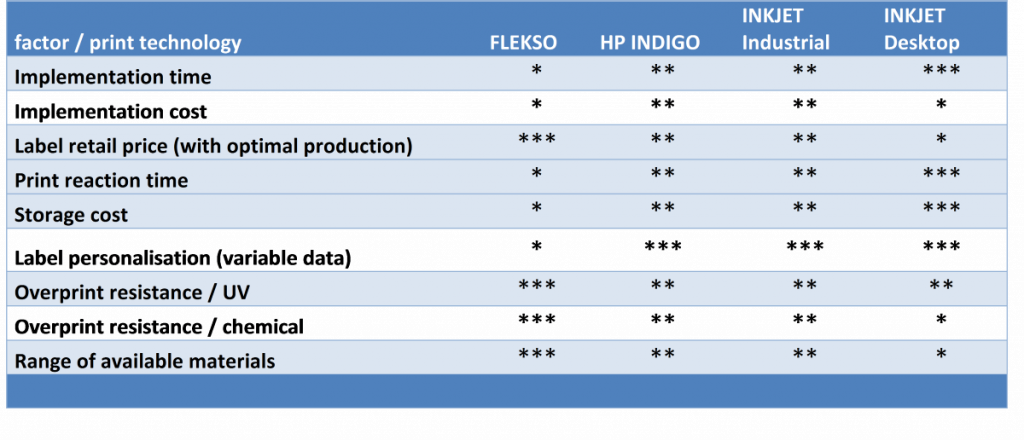
* – poor
** – well
*** – very well
[1] The Future of Global Inkjet Printing to 2021. Smiter Spira, 26.02.2016
[2] Etisoft recommends programs for inkjet colour label printing in connection with a much wider range of options for print management than from the device driver position.
(235)